
Enquiries
Let us know your requirements and we will get in touch to provide no obligation assessments.
Heat Pumps – How They Work?
A heat pump heating system consists of 3 components:
the heat source, the heat pump itself and a heat distribution and storage system.
Heat pumps are able to produce more energy than they consume by using the conventional refrigeration cycle to absorb heat from the environment and raise it to a suitable level for heating and hot water
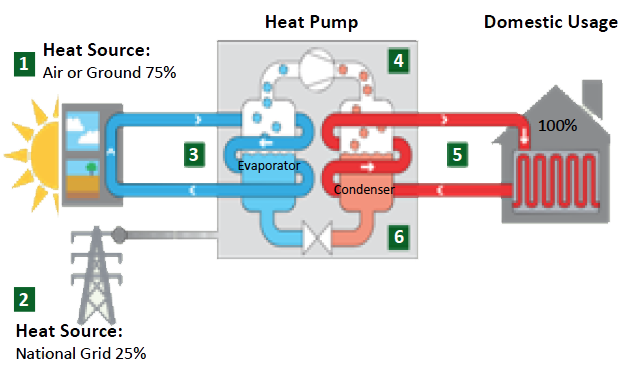
1.
75% of the energy is taken from the environment i.e. the air or ground and transferred to the heat pump.
2.
25% of the energy is sourced from the national grid in the normal way of supplying your electricity. This is used to operate the heat pump but with very low consumption.
3.
Energy from the source is transferred to the refrigerant inside the heat pump’s evaporator. This causes the temperature of the refrigerant to rise and change state from liquid to gas.
4.
The refrigerant gas is then compressed, using an electrically driven compressor, reducing its volume and causing its temperature to rise significantly.
5.
5. A heat exchanger (condenser) then extracts the heat energy from the hot refrigerant to heat water for central heating, underfloor heating or domestic hot water.
6.
After giving up its heat energy the refrigerant turns back into a liquid and is able to absorb energy from the environment, allowing the cycle to begin again.




